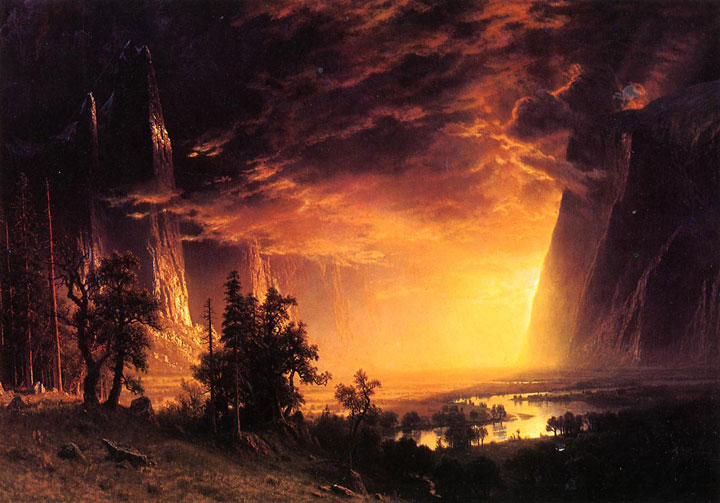
The day after John Steinbeck’s recent birthday, I spoke to an audience at the University of Oklahoma in Norman, where I teach, about three forgotten stories behind the writing, impact, and unintended consequences of The Grapes of Wrath. The occasion was an exhibition of works by the Great Depression photojournalist Horace Bristol, one of Steinbeck’s collaborators in the run-up to The Grapes of Wrath.
The day after John Steinbeck’s recent birthday, I spoke to an audience at the University of Oklahoma in Norman, where I teach, about three forgotten stories behind the writing, impact, and unintended consequences of The Grapes of Wrath. The occasion was an exhibition of works by the Great Depression photojournalist Horace Bristol, one of Steinbeck’s collaborators in the run-up to The Grapes of Wrath.
The venue was the Fred Jones Museum of Art at the University of Oklahoma, which figures significantly in the narrative behind John Steinbeck’s novel. Steinbeck may not have visited the state before he wrote The Grapes of Wrath, but Oklahoma cared deeply about his work—and not just in the negative way portrayed by the press. Closer consideration of John Steinbeck, his collaborators, and his fictionalized migrants seemed appropriate in preparing my talk as I contemplated the 75th anniversary of The Grapes of Wrath. What I uncovered wasn’t new but hidden. Here is a summary of my remarks to my University of Oklahoma audience.
Unequal Collaborators: John Steinbeck and Horace Bristol
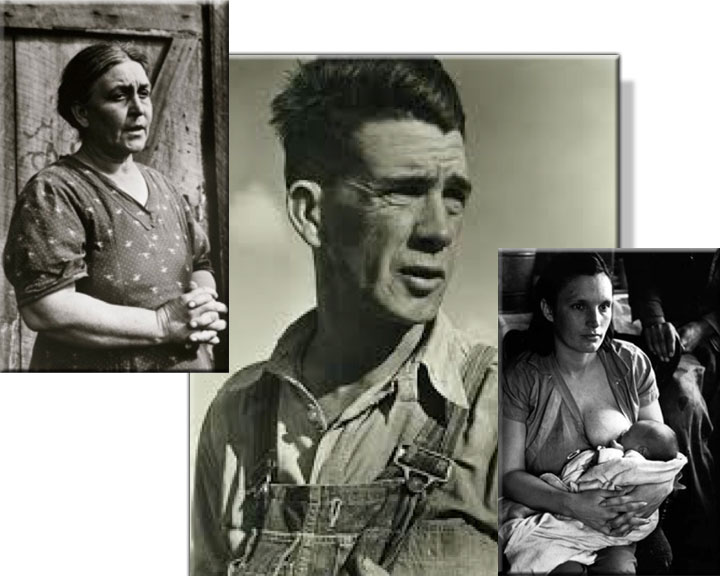
Traveling on weekends on assignment for Life magazine from the end of 1937 to March 1938, Horace Bristol accompanied John Steinbeck to migrant camps in California’s Central Valley. The Steinbeck-Bristol partnership proved less than equal. Bristol needed the collaboration with Steinbeck more than the writer needed the photographer.
In Dubious Battle, the 1936 novel in which Steinbeck charted the anatomy of a Central Valley fruit pickers’ strike, hit sore nerves at both ends of America’s political spectrum and attracted noisy criticism from communists and conservatives alike. In August he moved on to the San Joaquin Valley to examine the living conditions of California migrant workers and their families for the left-leaning San Francisco News. His hard-hitting account of the struggle for survival of Great Depression migrants from the country’s ravaged heartland was serialized in the paper under the title “The Harvest Gypsies.” It was reprinted (with an additional chapter) in pamphlet form by the Simon J. Lubin Society in 1938 under the title Their Blood is Strong, with revenues going to migrant relief.
The Steinbeck-Bristol partnership proved less than equal. Bristol needed the collaboration with Steinbeck more than the writer needed the photographer.
Steinbeck’s 1937 novella Of Mice and Men—the searing story of the daily labors, fragile hopes, and ultimate tragedy that befall the itinerant ranch hands George and Lennie—became a national sensation; the New York stage version played to critical acclaim and ran for more than 200 performances. Clearly, Horace Bristol saw the professional benefits of collaborating with John Steinbeck, despite differences. Like the writer, however, the photographer was drawn on a deeply personal level to the suffering migrants they observed living in tents, makeshift shacks, and broken down vehicles, hidden along California’s byways and back roads.
The Horace Bristol-John Steinbeck collaboration for Life resulted in unforgettable examples of Great Depression photojournalism. But Bristol’s goal for the project—a book of his photographs accompanied by Steinbeck’s text—never materialized. By late May, Steinbeck had begun the hectic hundred days of writing that produced The Grapes of Wrath: Steinbeck’s sprawling manuscript, completed in November, was published in April 1939 to acclaim and attack. Clearly, one reason the Bristol-Steinbeck partnership never achieved full fruition is that Steinbeck was too busy writing his novel and dealing with the celebrity and controversy that ensued.
But there is another reason: John Steinbeck could be an undependable collaborator. A proposed partnership with the photojournalist Dorothea Lange, whose pictures of Great Depression migrants deeply moved the author, also failed to materialize. And there was a third reason, too: Life refused to publish the text written by Steinbeck to accompany Bristol’s photographs. Although some of Bristol’s pictures appeared, the author’s language was too liberal for the magazine’s conservative tastes. John Steinbeck’s relationship with the Time-Life publishing empire never recovered; almost without exception, his books were panned by Time’s reviewers, despite the Pulitzer Prize he received for The Grapes of Wrath and the Nobel Prize for Literature he was awarded in 1962.
John Steinbeck could be an undependable collaborator. A proposed partnership with the photojournalist Dorothea Lange, whose pictures of Great Depression migrants deeply moved the author, also failed to materialize.
It is also worth noting that, while Steinbeck appreciated the visual arts and understood the power of words wedded to images, as a writer he may have doubted that documentary photography was the most desirable medium to illustrate his powerful prose. Indeed, as pointed out by James Swensen—whose manuscript “Picturing Migrants” is scheduled for publication by the University of Oklahoma Press—the 1939 dust jacket of The Grapes of Wrath featured, not a real-life image by Bristol, Lange, or any of the other Farm Security Administration photographers documenting the Great Depression in disturbing detail, but a made-to-order painting by the commercial illustrator Elmer Hader. To the chagrin of Ron Stryker, head of the Historical Section of the Farm Security Administration, the deluxe two-volume version of The Grapes of Wrath published in 1940 by Viking Press featured a series of paintings by the Midwestern artist Thomas Hart Benton, not the photographs of Bristol, Lee, or Lange.
As a writer he may have doubted that documentary photography was the most desirable medium to illustrate his powerful prose.
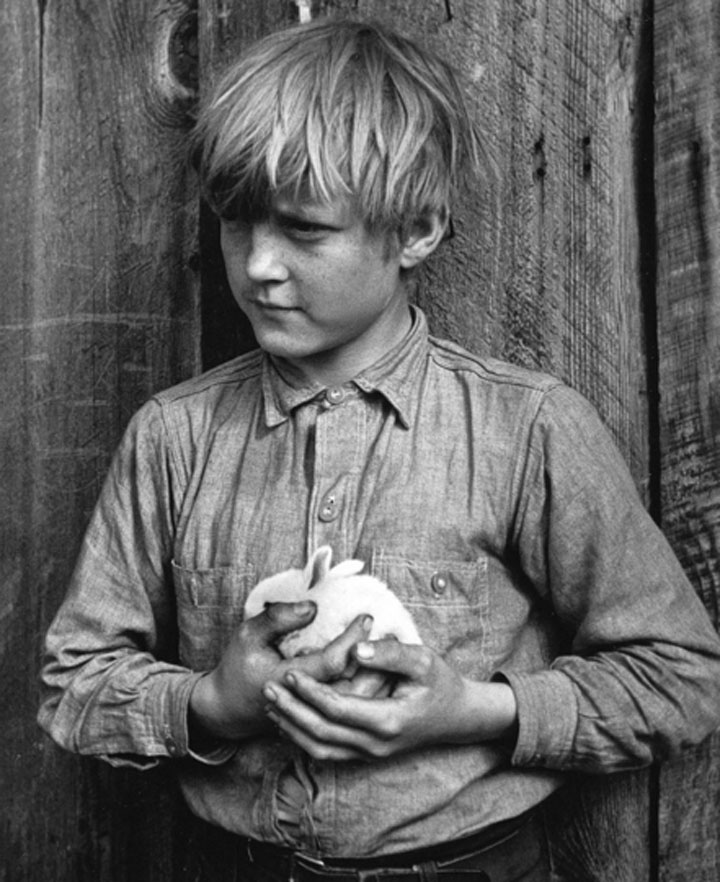
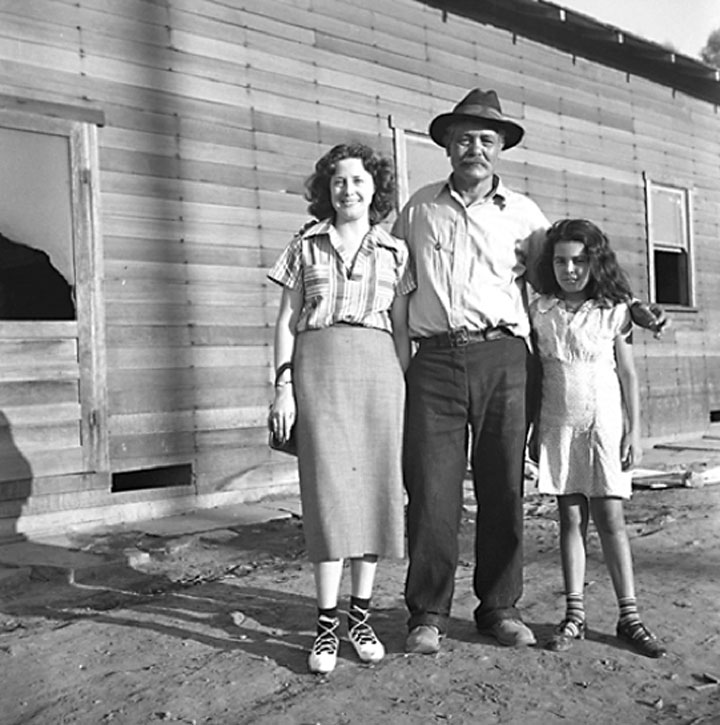
The pictures Bristol took on his travels with Steinbeck became famous anyway, thanks to their publication—along with images by Lange—in the April 1939 issue of Fortune and the June issue of Life, popular magazines with wide readership. As a result, Bristol’s photographs were used by the director John Ford in casting and costuming Ford’s award-winning movie adaptation of The Grapes of Wrath, released in January 1940. A second Life magazine article followed a month later. It featured Bristol’s “Joads” (shown above and at the top of the page) and the movie’s characters (shown below), displayed side by side with the telling tag, “Speaking of Pictures. . . these by Life prove facts in ‘Grapes of Wrath.’” However reluctantly the editors recognized the truth of Steinbeck’s book, they never approved of its author.
Russell Lee, The Grapes of Wrath, and a Great Depression Photography Exhibition at the University of Oklahoma
Now to an unfamiliar twist in this oft-told tale, one that is explored by James Swensen in his forthcoming study for the University of Oklahoma Press. To capitalize on the success of John Steinbeck’s novel and John Ford’s film, Ron Stryker’s Historical Section began mounting Grapes of Wrath exhibitions of work by the agency’s various photographers—with text taken from the novel—showing the conditions in Oklahoma and other parts of America’s Southern Plains that precipitated the exodus of native farm families, the problems they faced on the road, and their plight once they reached California. In March 1940, an FSA exhibition of 48 works by Russell Lee, Dorothea Lange, Arthur Rothstein, and Ben Shahn (although none by Horace Bristol) appeared in the University of Oklahoma’s Memorial Student Lounge, sponsored by the departments of Sociology and Anthropology.
Willard Z. Park, an Anthropology Department faculty member, was the person most responsible for bringing the exhibition to campus. Park—whose brief tenure at the University of Oklahoma lasted from 1938 to 1942—was also part of a faculty group that purchased four copies of The Grapes of Wrath for the university library to help meet demand for the book—more than 100 University of Oklahoma students were on the waiting list to check out John Steinbeck’s novel. Swensen notes that in the wake of the campus exhibit “several [University of Oklahoma] students made trips to a local migrant colony in Norman, called ‘Tower Town,’ to see the plight of the migrants themselves.” Tower Town was located near 804 East Symmes Street, just east of Porter Avenue.
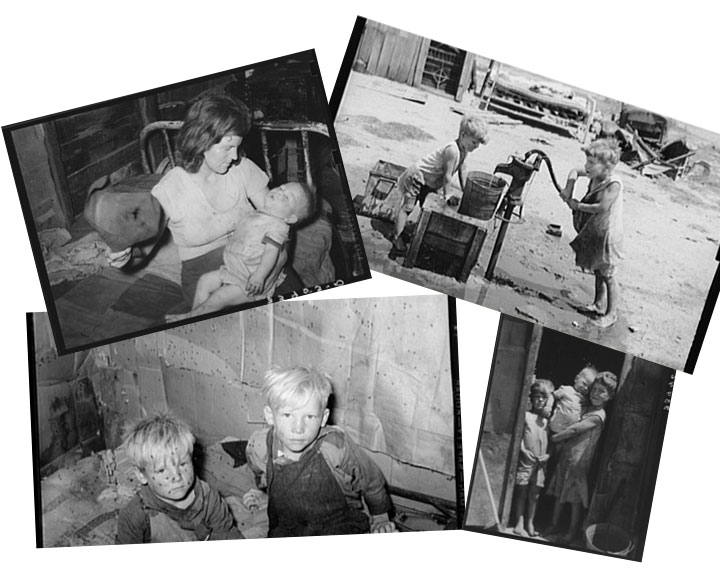
As poor as living conditions were for some Norman residents, Swensen explains that the FSA photographers who documented the plight of displaced Oklahomans during the latter years of the Great Depression traveled instead to the banks of the Canadian River in Oklahoma City, where more than 3,000 homeless Oklahomans had camped out. The University of Oklahoma Grapes of Wrath exhibition featured photographs of the Oklahoma City camps made by Russell Lee in 1939. Four examples of Lee’s harrowing images are shown above. They bear visual witness to Henry Hill Collins’ description of Oklahoma poverty in his 1941 book America’s Own Refugees: Our 400,000 Homeless Migrants (Princeton University Press):
Many of the inhabitants of this camp, a rent-free shack-town fashioned over and out of a former dump, were drought and tractor refugees from farms elsewhere in the State. . . . The ‘Housing’ . . . was almost entirely pieced together out of junk-yard materials by the unfortunates . . . . Neither camp provided sanitary facilities; children, looking like savages, played in the dumps, wandered along the neighboring, muddy banks of the half-stagnant Canadian River. . . . [S]o foul were these human habitations and so vast their extent that some authorities reluctantly expressed the belief that Oklahoma City contained the largest and worst congregation of migrant hovels between the Mississippi River and the Sierras.
Whose Names are Unknown: Oklahoma’s Forgotten Novel
Our next story concerns a Great Depression novel written at the time of The Grapes of Wrath that remained unpublished until 2004. Its author was the remarkable Oklahoma native Sanora Babb. Born in the Territory’s Otoe Indian community in April 1907, seven months before Oklahoma became a state, Babb was living in California in 1938 and working for the Farm Security Administration. A contemporary of John Steinbeck, she actually met the author twice. She also kept detailed notes on what she observed in the California camps, copies of which were loaned by her boss Tom Collins—the man to whom Steinbeck dedicated The Grapes of Wrath—along with the meticulous reports Collins wrote about Oklahoma migrant culture and dialect.
John Steinbeck used Collins’ anecdotes and statistics to research The Grapes of Wrath. Sanora Babb used the stories she gathered to write her own novel, Whose Names are Unknown. Its title and subject attracted the attention of Bennett Cerf, the editor at Random House, who wanted to publish her book. Cerf abandoned his plans when The Grapes of Wrath became an overnight bestseller, another collateral casualty of John Steinbeck’s phenomenal success. When Babb approached Pascal Covici, Steinbeck’s loyal editor at Viking, he also declined.
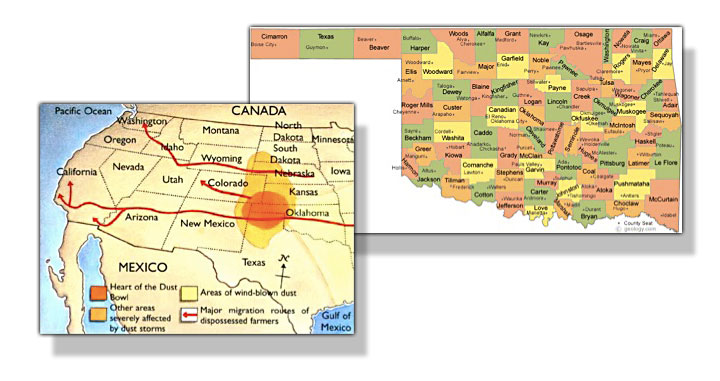
As a result, Whose Names are Unknown was unread for 65 years years before being published by the University of Oklahoma Press. But Babb’s book stands on its own feet as a classic of Great Depression fiction with significant differences from Steinbeck. While The Grapes of Wrath deals with migrants from far east-central Oklahoma—Sallisaw, in Sequoyah County, which was affected by drought and decline but wasn’t a Dust Bowl environmental disaster—Babb’s novel is set in Cimarron, the state’s westernmost county, roughly 450 miles from Sallisaw and squarely within the area of America’s Dust Bowl devastation. Unlike the author of The Grapes of Wrath, Babb was an Oklahoma native who experienced extreme poverty as a child and knew her people and their land firsthand.
Whose Names are Unknown was unread for 65 years before being published by the University of Oklahoma Press.
Babb had moved to California in 1929 to take a job at the Los Angeles Times. When she arrived the stock market had crashed, the Great Depression had begun, and the promised job dried up. A migrant without a home, she slept in a city park before leaving for Oklahoma in the mid-1930s, where she witnessed the terrible poverty gripping her native state. Eventually she returned to California to work for the FSA, serving migrant families stranded without a home or a job, just as she had been years earlier. In contrast, John Steinbeck gained much of his understanding of Great Depression conditions in Oklahoma second hand, through reading reports by federal aid workers like Babb and Collins and from his experience delivering food and aid to California migrants from the Southern Plains.
Still, the John Steinbeck-Sanora Babb story sounds like a classic smash-and-grab: celebrated California author steals the material of unknown Oklahoma writer, resulting in his financial success and her failure to get her work published. Ken Burns’ 2012 documentary The Dust Bowl touches on the subject, devoting space to Babb’s life and book in The Grapes of Wrath’s giant shadow. But Steinbeck absorbed field information from many sources, primarily Tom Collins and Eric H. Thomsen, regional director of the federal migrant camp program in California, who accompanied Steinbeck on missions of mercy.
As noted, John Steinbeck acknowledged Collins’ importance in his research for The Grapes of Wrath, although his promise to write an introduction and help Collins’ get his reports published failed—not unlike John Steinbeck’s book project with Horace Bristol. If Steinbeck read Babb’s extensive notes as carefully as he did the reports of Collins, he would certainly have found them useful. His interaction with Collins and Thomsen—and their influence on the writing of The Grapes of Wrath—is documented because Steinbeck acknowledged both. Sanora Babb went unmentioned.
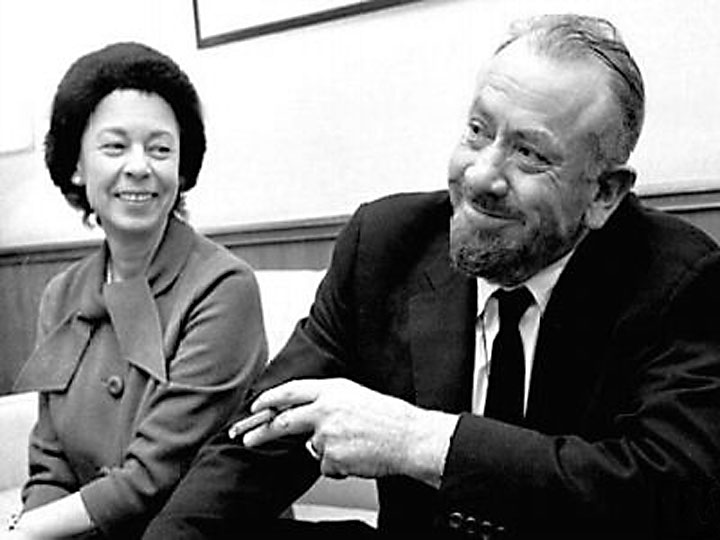
Whose Names are Unknown was published by the University of Oklahoma Press shortly before Babb (shown above hanging wash with Tom Collins, standing beside an identified labor organizer and girl, and sitting with a group of migrants) passed away at 98. Like The Grapes of Wrath, Babb’s novel is must-reading for serious students of the Dust Bowl and Great Depression in Oklahoma. Its primary characters are Julia and Milt Dunne, an Oklahoma couple with two daughters—Lonnie and Myra—who are caught outside with their pregnant mother when a sudden storm blows up and Julia takes a fall. As a result, Julia’s third child is still-born, like Rose of Sharon’s infant in The Grapes of Wrath, and Milt buries the baby in the yard. Rose of Sharon’s abandonment by her husband in Steinbeck’s story is physical. Julia’s growing distance from Milt Babb’s narrative is psychological:
Sometimes Julia thought of the little boy who was so nearly born, saying in her mind it was better that he was dead, but in spite of this reasonable comfort, she felt the monotonous ache of grief and of Milt’s frustration. That peculiar ripening joy she had felt—with the child filling her and moving strongly with his secret life—had left her. The emptiness of her womb crept into her emotions, and she went through the days and nights feeling numb and alone. Milt was morose and easily angered, and although he spoke of the boy only once or twice, she felt coming from him some undetermined blame toward her.
Parallel Migrations: The Southern and the Northern Plains
Unlike our focus on two novels and two photographers in exploring the background of The Grapes of Wrath, our view of their Great Depression context requires a wide-angle perspective on the contrasting demographics of migration patterns from the Great Plains to the promised lands of the American West in the 1930s. I say promised lands because migration to California from Oklahoma and other Southern Plains states wasn’t the only instance of mass westward movement during the decade recorded in John Steinbeck and Sanora Babb’s writing and the photographs made by Horace Bristol and Russell Lee.
James Gregory, the preeminent historian of the migration of Southwesterners to California during the Great Depression, places the total figure for out-migration to the Golden State in the 1930s from the Arkansas, Missouri, Oklahoma, and Texas at 315,000-400,000. (California received about a million American migrants during the decade, and they came from all over America, not just the Southern Plains.) Notably, fewer than 16,000 of these Great Depression refugees—less than six percent of the total number of migrants from the four states mentioned who ended up in California—came from the area of the Dust Bowl. Gregory notes that journalists of the period are primarily to blame for “confusing drought with dust” and oversimplifying the facts: “the press created the dramatic but misleading association between the Dust Bowl and the Southwestern migration.” The subtitle of Gregory’s excellent book—American Exodus: The Dust Bowl Migration and Okie Culture in California (Oxford University Press, 1991)—makes this critical point.
Migration to California from Oklahoma and other Southern Plains states wasn’t the only instance of mass westward movement during the decade recorded in John Steinbeck and Sanora Babb’s writing and the photographs made by Horace Bristol and Russell Lee.
So it isn’t surprising that the role played by Oklahoma and its residents looms so large in the public memory of the Southern Plains migration to California during the Great Depression. The Federal Writers Project’s publication Oklahoma: A Guide to the Sooner State (1941) reported that half of the state’s population was on relief by the late 1930s. In his remarkable 1942 study, Ill Fares the Land: Migrants and Migratory Labor in the United States, California’s progressive journalist Carey McWilliams stated that by 1935, “61.2 per cent of farms in Oklahoma were operated by tenants” and between 1935 and 1940 Oklahoma lost a total of 32,000 farms or more at a rate of 18 per day. Moreover, McWilliams noted, from July 1, 1935 to June 30, 1939, almost 71,000 Oklahomans crossed the Arizona border into California. Interestingly, the bulk of this exodus came from Oklahoma’s populous central counties; the four counties with the highest number of outbound migrants were Oklahoma, Caddo, Muskogee, and Tulsa.
As Oklahomans, Californians, and readers of The Grapes of Wrath quickly learned, the term “Okie” became a derisive identifier for all migrants to California, not only from Oklahoma but from other Southwestern states as well. “Little Oklahoma” was the local name for the Alisal, the area east of John Steinbeck’s hometown of Salinas where white migrants from the Plains states were clustered, out of sight and out of mind of respectable Salinians—as Steinbeck noted in his letters and in L’Affaire Lettuceberg, the angry satire he wrote (and destroyed) before beginning The Grapes of Wrath.
‘Okie’ became a derisive identifier for all migrants to California, not only from Oklahoma but from other Southwestern states as well.
Even today, it is hard to avoid perpetuating the “Okie” and “Dust Bowl” stereotypes and the oversimplifications that they represent. These became so pervasive that historians of the Great Depression have paid little attention to a parallel migration of similar size—approximately 300,000 individuals—from the Northern Plains states of Nebraska, South Dakota, and North Dakota to the Pacific Northwest states of Washington, Oregon, and Idaho. One historian, Rolland Dewing, has helped correct the record, explaining that Northern Plains migrants left their home states because of drought conditions and economic collapse, much like their counterparts to the south. In Regions in Transition: The Northern Great Plains and the Pacific Northwest in the Great Depression (University Press of America, 2006), Dewing notes that approximately two-fifths came from North Dakota, two-fifths from South Dakota, and one-fifth from Nebraska.
Steinbeck’s Oklahomans and America’s “Other Migrants”
But as massive in scale as the migration from the Northern Plains to the Pacific Northwest became during the Great Depression, the particulars of this phenomenon have for a variety of reasons remained largely forgotten. As Rolland Dewing explains in his book, there was no agribusiness equivalent to California’s Central and Imperial valleys in the Pacific Northwest—no foundation for the systematic economic exploitation and mistreatment of the newcomers.
The Northwest timber industry was doing quite well as the Northern Plains economy collapsed, and this stability—along with other positive economic factors in Washington, Oregon, and Idaho—helped ease the transition of Northern Plains migrants, which peaked in 1936, when the economy of the host region was picking up. Because the population of the Pacific Northwest was aging at the time of the Great Depression, younger migrants were welcomed by many as a demographic addition, unlike those arriving in California from Oklahoma and other Southern Plains states, like the Joads in The Grapes of Wrath.
Because the population of the Pacific Northwest was aging at the time of the Great Depression, younger migrants were welcomed by many as a demographic addition, unlike those arriving in California from Oklahoma and other Southern Plains states, like the Joads in The Grapes of Wrath.
Then, too, the socioeconomic and educational levels of Northern Plains migrants were closer to those of the Pacific Northwest states, so newcomers and hosts shared more in common than Southern Plains migrants did with less friendly Anglo-Californians. Indeed, many residents of the Pacific Northwest had been born or maintained family roots in the upper-Midwest: Northern Plains migrants seemed more alike than different in background and behavior to their hosts.
Like Steinbeck’s migrants in The Grapes of Wrath, Northern Plains residents suffered terribly during the Great Depression. South Dakota, for example, experienced a seven percent population decline in the 1930s. The population loss for Oklahoma was much less: the state’s population was 2,396,040 in 1930 and 2,336,434 in 1940 (a 2.5 percent decline). But migrants from the Northern Plains to the Pacific Northwest never experienced suffering on the scale of their southern counterparts who migrated to California. No one wrote a Grapes of Wrath about them. As a consequence their stories have been largely forgotten.
Rescuing Sanora Babb from John Steinbeck’s Shadow
Horace Bristol and Russell Lee were among the most important documentary photographers of Great Depression America. Like the pictures of migrant mother and children made by Dorothea Lange, their images helped sear the truth behind The Grapes of Wrath into America’s collective consciousness. The photographs Bristol took on assignment with Steinbeck for Life proved essential to the casting and costuming of the Joads in the movie version of the novel. But if The Grapes of Wrath hadn’t been so successful, Sanora Babb’s novel of Oklahoma would probably have been published as promised and might have become a Great Depression classic being celebrated, like The Grapes of Wrath, on its 75th anniversary.
Finally, if Steinbeck’s timeless prose—along with photographs by Bristol, Lee, and Lange and John Ford’s movie—hadn’t evoked the Southern Plains exodus to California so powerfully for Americans living through the Great Depression, our memory of migration in the 1930s might include the parallel movement of Northern Plains refugees to the Pacific Northwest. But the migration of these displaced Americans wasn’t chronicled by a John Steinbeck or a Sanora Babb: their suffering was on a smaller scale and they encountered less hostility. Thus art copies history but also reflects it. New light on Great Depression migration and the forgotten background of The Grapes of Wrath from the University of Oklahoma further illuminates Steinbeck’s masterpiece. It also helps rescue a forgotten work, written by a native Oklahoman, from the shadow of a greater writer.
SteinbeckNow.com is proud to publish David Wrobel’s feature as the 80th post produced by our website in its first eight months. A scholar of United States history, David is also an avid reader and deep thinker on the writing of John Steinbeck. He contributed a chapter about Steinbeck’s social-protest fiction to Regionalists on the Left, an anthology of essays edited by Michael C. Steiner, and he gave a lecture, John Steinbeck’s America: A Cultural History of the Great Depression and World War II, to a large audience at the University of Oklahoma’s 2013 Teach-In on the Great Depression and World War II. He is currently working on “John Steinbeck’s America: A Cultural History, 1930-1968.”